Raghu On Tech
Pro tips on managing data at scaleAlternative(s) To db2cluster command To Display GPFS Configuration

While working in a pureScale environment, I learned that db2cluster command is not the quickest way to get the information you are looking for. If you are working on troubleshooting a problem, waiting for db2cluster command to return the output could be frustrating. Depending on the state of your pureScale cluster it is possible that db2cluster command could hang indefinitely. It is during those circumstances, I learned to circumvent db2cluster command and use native GPFS, TSA/RSCT commands…
db2cluster command behind the scenes is really a wrapper on a bunch of GPFS and RSCT commands.
I am going to list some of the commands that I use from time to time to save time and get the information that I need quickly. If you keep the default configuration for GPFS and other components of the pureScale, you should see any GPFS related commands under “/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin” directory.
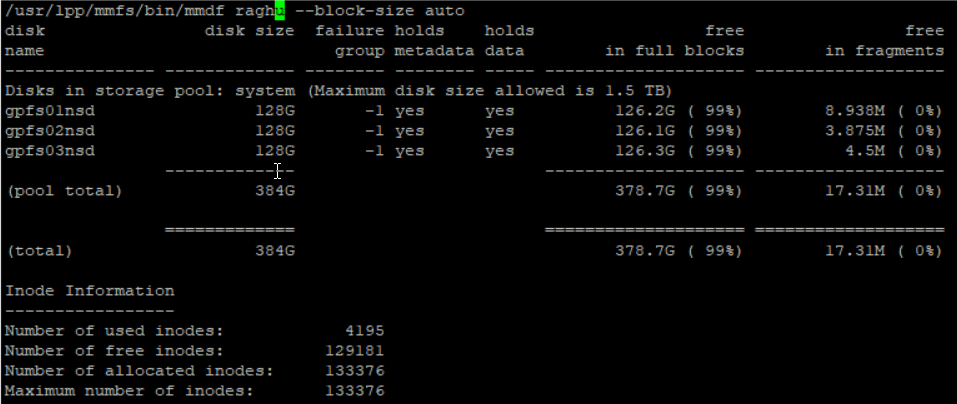
Finding disks associated with a GPFS filesystem:
mmdf command is your friend here. –block-size option will give you the free block information in a user friendly format such as GB instead of KB. Listing disks associated with the GPFS filesystem(s) is slow in general.
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmdf raghu --block-size auto
Finding GPFS Filesystem Properties/Attributes:
mmlsfs command will provide you a lot of information such as blocksize, remember default like shown below is 1 MB blocks i.e. OS will read 1 MB blocks to service a single IO request. It does not really matter what page size you specify at the tablespace level, OS always does IO at filesystem block size. So it may be worth experimenting your workload with smaller block sizes and measure the performance impact.
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmlsfs raghu

Listing all available NSD disks:
If you are looking to list all the available shared disks on the cluster, then use mmlsnsd command.
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmlsnsd

Displaying GPFS and its manger node/host info:
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmlsmgr

How to display GPFS cluster information ?
You may use mmlscluster command to get the information on GPFS cluster itself, such as its name, participating nodes, remote shell and file copy protocols used by GPFS etc.
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmlscluster

Determining status of disks in a GPFS:
If you are trying to get status of individual disks under a GPFS file system, you may use mmlsdisk command as shown below. It will give you the the status, ID and quorum information of the disks under a GPFS.
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmlsdisk raghu1 -d "gpfs01nsd;gpfs02nsd;gpfs03nsd" -L

Displaying GPFS configuration:
Last but not least, one of my favorite GPFS commands is mmlsconfig, it provides you the configuration parameters that were changed as part of the GPFS cluster setup as well as the filesystems that are part of the GPFS cluster. It also list tiebreaker disk name etc.
/usr/lpp/mmfs/bin/mmlsconfig

I will write another blog in future on using native TSA/RSCT commands to display some pureScale cluster manager configuration information.
What other GPFS commands would you use frequently, other than the ones that I listed above ? Please respond in the comments and I would love to hear back from the peers.

 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
0 Comments